
introduction
This standard is drafted in accordance with the provisions given in GB/T 1.1-2009.
Please note that some aspects of this document may involve patents. The publisher of this article assumes no responsibility for identifying these patents.
This standard is proposed by the State Food and Drug Administration.
This standard is formulated by the National Technical Committee for Standardization of Medical Infusion Devices (SAC/TC 106).
This standard is drafted by Lubrizol Management (Shanghai) Co., LTD., Covestro Polymers (China) Co., LTD., Shandong Medical Device Product Quality Inspection Center.
The main drafters of this standard: Bai Bing, Bo Xiaowen, Yan Ge, Li Yi.
Application of Lubrizol polymer tablet drug release mechanism
introduction
Medical thermoplastic polyurethane has good extensibility and deflection resistance, high strength, wear resistance, good biocompatibility, and polyurethane material has good physical and mechanical properties and processing properties, so that it is widely used in the medical field, such as the sleeve and extension tube of intravenous indwelling needle, drip tube of infusion set, dropper, pipeline, etc.
Based on the synthesis process of polyurethane pellets, there may be residual diisocyanate monomer in the pellets. It is also possible to produce such monomers during its processing. It has been reported that residual monomers and their hydrolyzed products have certain toxicity.
Text content
Step 1: Scope
This standard specifies the technical requirements, test methods, marking, packaging and storage of thermoplastic polyurethane special materials (TPU) for medical infusion, blood transfusion and injection equipment.
This standard applies only to polyurethane special materials with a single component, and does not apply to polyurethane special materials that are blended with polyurethane special materials (such as polyurethane/polyvinyl chloride, polyurethane/polyformaldehyde, etc.) and added with other ingredients (such as developer, colorant, glass fiber, etc.).
Application of Lubrizol polymer tablet drug release mechanism
2. Normative reference documents
The following documents are essential for the application of this document. For dated references, the date-only version applies to this document. For undated references, the latest version (including all amendment orders) applies to this document.
GB/T 528-2009 Vulcanized or thermoplastic rubber -- Determination of tensile stress-strain properties GB/T 529-2008 Vulcanized or thermoplastic rubber -- Determination of tear strength (pants, right Angle and crescent shaped specimens) GB/T 1040. 1-2006 Determination of tensile properties of plastics - Part 1: General GB/T 2411-2008 Indenting hardness (Shohr hardness) of plastics and ebonites using a durometer GB/T 2918-1998 Standard environment for state regulation and testing of plastic specimens GB/T 3398. 2-2008 Hardness testing of plastics Part 2: Rockwell hardness GB/T 6682-2008 Analytical laboratory water specifications and test methods GB/T 9352-2008 plastic thermoplastic material specimen compression molding
Instruments for infusion, transfusion and injection for medical purposes - Part 1: Chemical analysis GB/T 16886. Biological evaluation of medical devices - Part 1: Evaluation and testing GB/T 17037. 1-1997 Preparation of injection test samples for thermoplastic materials - Part 1: General principles and preparation of multipurpose test samples and strip test samples Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China (2015 Edition IV)
Step 3: Requirements
3.1 Authentication
According to the 2015 edition of the Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China, the infrared spectrum of medical polyurethane materials should be consistent with the spectrum provided by the manufacturer.
3.2 Appearance
According to 4.3, the special materials for medical polyurethane are uniform particles without foreign impurities.
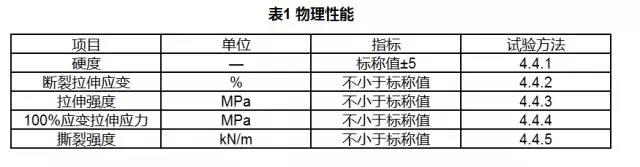
3.3 Physical Properties
The physical properties of medical polyurethane materials shall comply with the provisions of Table 1.
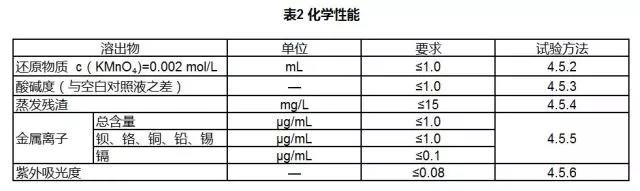
3.4 Chemical Properties
The chemical properties of medical polyurethane special materials shall comply with the provisions of Table 2
3.5 Biocompatibility
GB/T 16886. When biological evaluation of medical polyurethane materials is carried out, the evaluation results should indicate that there is no unacceptable biological hazard.
Note: The biological test methods specified in GB/T 14233.2 should be considered to supplement the methods specified in GB/T 16886. Biological evaluation should be based on the specific conditions of the device intended to be manufactured from the material and the sterilization process to which it is subjected.
4. Test methods
4.1 Preparation of sample
The physical properties of the test using the compression test, the preparation according to GB/T 9352-2008 regulations. Biological evaluation can also be made by injection molding test plates, which are prepared according to GB/T 17037. Provisions of 1-1997.
Note: In order that the test results are representative of the performance of the final device, the test piece may be prepared and subjected to the sterilization process expected of the medical device.
Application of Lubrizol polymer tablet drug release mechanism
4.2 State adjustment of the sample and standard environment of the test
The state adjustment of the sample is carried out in accordance with the provisions of GB/T 2918-1998, the condition of the state adjustment is the level 2 standard environment (23/50), and the adjustment time is at least 40h, but not more than 96h.
4.3 Appearance
Observe with normal or corrected vision under natural light or fluorescent lamps.
4.4 Physical Performance
4.4.1 Hardness
For special materials with nominal hardness less than 85D, test pieces are taken according to GB/T 2411-2008. The hardness tester uses Shore A and the applied load is 1.00kg±0. When the indicator value of type A hardness tester is greater than 90, type D hardness tester is used, and the load is 5.00kg±0. 01kg. For special materials with nominal hardness greater than 100D, take the test piece according to GB/T 3398. 2-2008 Test. The number of test sites shall not be less than 5.
4.4.2 Tensile strain at fracture
Prepare the test piece according to 4.1, and adjust the state of the test piece according to 4.2.
Take the adjusted test piece, prepare the sample according to GB/T 528-2009 type 1 sample, according to GB/T 1040. 1-2006 Test, test speed 200mm/min.
4.4.3 Tensile strength
Prepare the test piece according to 4.1, and adjust the state of the test piece according to 4.2.
Take the adjusted test piece, cut the sample piece according to GB/T 528-2009 type 1 sample, according to GB/T 1040. 1-2006 Test, test speed 200mm/min.
4.4.4 100% strain tensile stress
Prepare the test piece according to 4.1, and adjust the state of the test piece according to 4.2.
Take the adjusted test piece, cut the sample piece according to GB/T 528-2009 type 1 sample, according to GB/T 1040. 1-2006 Test, test speed 200mm/min.
4.4.5 Tear strength
Prepare the test piece according to 4.1, and adjust the state of the test piece according to 4.2.
Take the adjusted test piece, cut the sample piece according to the right-angle unnotched sample in GB/T 529-2008, and test according to GB/T 529-2008, the test speed is 500mm/min.
4.5 Chemical properties of the solution
4.5.1 Preparation of test solution
The granulated material was weighed, washed with water in accordance with the secondary test of GB/T 6682-2008, and water was added according to the ratio of mass (g) to water (mL) of 1:5, at 37 ° C ±1 ° C for 72h, the sample was separated from the liquid, and the sample was cooled to room temperature. The same batch of water was taken to prepare the blank contrast solution by the same method.
4.5.2 Reducing substances
The test solution and control solution prepared in 4.5.1 were obtained according to 5.2 in GB/T 14233.1-2008. 2 Perform the test.
4.5.3 pH
The test solution and control solution prepared in 4.5.1 were obtained and tested according to 5.4.1 in GB/T 14233.1-2008.
4.5.4 Evaporation residue
The test solution and control solution prepared according to 4.5.1 were taken and tested according to 5.5 in GB/T 14233.1-2008.
4.5.5 Metal ions
Take the test solution prepared in accordance with 4.5.1, according to 5.6 in GB/T 14233.1-2008. 1 and/or Atomic absorption spectrophotometry (AAS) or equivalent method for testing.
4.5.6 UV absorbance
The test solution prepared in accordance with 4.5.1 was taken and tested in the wavelength range of 220nm-350nm as specified in 5.7 of GB/T 14233.1-2008.
5 flags
The mark on the packaging bag of medical polyurethane special materials should include the following:
a) Product name;
b) Manufacturer's name or trademark;
c) Model number;
d) Batch number;
e) Net weight.
6 Packaging and storage
6. 1 Packing
Medical polyurethane special materials should be at least double-layer packaging, packaging should ensure that the product is not contaminated during transportation and storage.
6. 2 Storage
Medical polyurethane materials should be stored in a warehouse that is ventilated, dry, clean and maintained with good fire protection facilities. Store away from heat source and avoid direct sunlight.
About us
Company Profile Honor Typical Case Corporate imageEquipment display
Powder forming class Medical devices Non standard customized equipmentNews Center
Company News Industry News FAQContact us
TEL: +86 0769-82263072 Contacts: +86 139 2924 7077/Mr. Wei Email: 13929247077@139.com Address: No. 31, Hulin Road, Huaide Community,Focus on us
 YeJet Mobile Station
YeJet Mobile Station WeChat official account
WeChat official account